
- #Can linux read ntfs install#
- #Can linux read ntfs driver#
- #Can linux read ntfs android#
And, because NTFS is designed to work with a Windows operating system, devices that operated from Mac or Android aren’t always compatible. The primary disadvantage of NTFS is that its modern capabilities aren’t accessible to older technology.
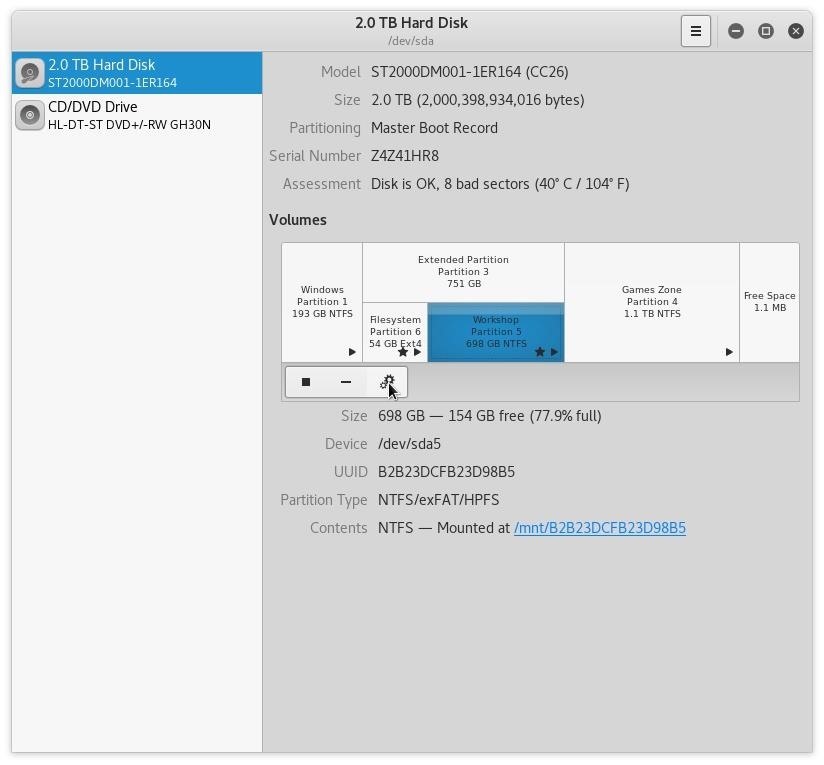
The number of disk accesses required to access a file. You can control the size of a cluster size based on what’s most important to your organization: The size of each cluster will range from 512 bytes to 64 kilobytes. Each file is distributed and stored in one or more clusters or disk spaces of a predefined uniform size (on the hard disk). Within each partition, the operating system tracks every file stored in a specific operating system.  A file gets divided into partitions within the hard disk. The technical breakdown of NTFS is as follow This log is called the Master File Table (MFT). File system journaling: This means that you can easily keep a log of-and audit-the files added, modified, or deleted on a drive. This feature enables businesses to have even more control over storage space. Disk space utilization: In addition to file compression, NTFS also allows disk quotas. Reliability: NTFS focuses on the consistency of the file system so that in the event of a disaster (such as a power loss or system failure), you can quickly restore your data. Security access control: NTFS will enable you to place permissions on files and folders so you can restrict access to mission-critical data. Performance: NTFS allows file compression so your organization can enjoy increased storage space on a disk. The benefits of NTFS are that, compared to other similar file systems like File Allocation Table (FAT) and High-Performance File System (HPFS), NTFS focuses on: NTFS was first introduced in 1993, as apart of the Windows NT 3.1 release.
A file gets divided into partitions within the hard disk. The technical breakdown of NTFS is as follow This log is called the Master File Table (MFT). File system journaling: This means that you can easily keep a log of-and audit-the files added, modified, or deleted on a drive. This feature enables businesses to have even more control over storage space. Disk space utilization: In addition to file compression, NTFS also allows disk quotas. Reliability: NTFS focuses on the consistency of the file system so that in the event of a disaster (such as a power loss or system failure), you can quickly restore your data. Security access control: NTFS will enable you to place permissions on files and folders so you can restrict access to mission-critical data. Performance: NTFS allows file compression so your organization can enjoy increased storage space on a disk. The benefits of NTFS are that, compared to other similar file systems like File Allocation Table (FAT) and High-Performance File System (HPFS), NTFS focuses on: NTFS was first introduced in 1993, as apart of the Windows NT 3.1 release. 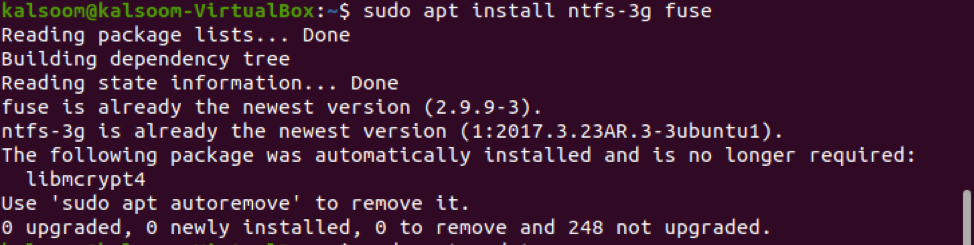
Locate your partition by the label you gave it when you formatted it, then tap it.NT file system (NTFS), which is also sometimes called the New Technology File System, is a process that the Windows NT operating system uses for storing, organizing, and finding files on a hard disk efficiently. In Ubuntu, for instance, open your file manager and click Other Locations. In most cases, you may need to give your distribution a “nudge” to mount the drive and allow you access.
#Can linux read ntfs install#
This is pre-installed with recent Ubuntu and Debian releases, but you may need to install it yourself in other distributions like Arch Linux.
#Can linux read ntfs driver#
Most modern Linux distributions will be able to read partitions with NTFS file systems, thanks to the ntfs-3g driver package. Once you’ve created your new partition and formatted it, you should be able to access it in Windows File Explorer. You can either right-click any existing partitions, click Delete Volume and then create a new partition in the “Unallocated” space, or you can choose Format to format an existing partition to the NTFS file system. If you’re using another hard drive, and need to delete or format any existing partitions, Disk Management will allow you to do so.
At the final stage, click Finish to begin the process of creating and formatting your new drive partition. You can access the Windows Disk Management tool by right-clicking the Windows Start button and clicking Disk Management. If you need to resize Ext4 or other Linux file systems, switch to using GParted instead. You will only be able to resize partitions that already use Windows-supported file systems like NTFS or FAT32 using the Disk Management Tool. It’s included as a package for installation in most Linux system repositories. GParted can be run from removable media like a USB drive, or by installing it to your Linux system. If you’d prefer, you can create or resize your partitions with GParted instead. There are several tools for formatting and partitioning drives that you can use on Windows, but the easiest solution is to use one that’s already included – the Windows Disk Management tool. If you need to create space for your shared drive, whether it’s on the hard drive carrying on your system partitions or on an entirely separate drive, you’ll need to resize your partitions first. If you already have the space available to you on an existing hard drive, or if you’re using the entire space on a second hard drive, you can skip straight to our Creating Your Partitions section. There are two options for you when you’re looking to create your shared drive.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
